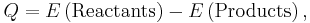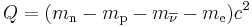Q value (nuclear science)
In nuclear physics and chemistry, the Q value for a reaction is the amount of energy released by that reaction:
A reaction with a positive Q value is exothermic (has a net release of energy), while a reaction with a negative Q value is endothermic (requires a net energy input).[1]
Q values are also featured in particle physics. For example in Sargent's rule, which states that the reaction rate of weak interactions is proportional to Q5. The Q value is the kinetic energy released in the decay of the particle at rest. For example, for neutron decay:[2]
where mn is the mass of the neutron, mp is the mass of the proton, mν is the mass of the electron antineutrino and me is the mass of the electron.
See also
Notes and references
- ^ K.S. Krane (1988). Introductory Nuclear Physics. John Wiley & Sons. p. 381. ISBN 047180553X.
- ^ B.R. Martin and G. Shaw (2007). Particle Physics. John Wiley & Sons. p. 34. ISBN 0-471-97285-1.
External links
- Nuclear Structure and Decay Data – IAEA with query on decays' Q-values